What is Carbon Fiber? Unveiling the Secrets of This “Magic Material”

Introduction
If you are interested in materials science, you have likely heard of carbon fiber. This revolutionary material is used in aerospace, automotive engineering, and even sports equipment, playing a crucial role in modern technology. But what exactly is carbon fiber? Why is it so widely used? In this article, we will explore the fascinating properties, manufacturing process, and applications of this "magic material."
Definition
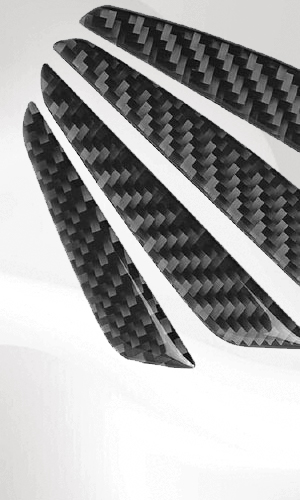
Carbon fiber is a high-performance material composed of carbon atoms arranged in a long, thin structure. Despite its lightweight nature, it exhibits exceptional strength and durability. The diameter of carbon fiber strands typically ranges from 5 to 10 micrometers, which is thinner than a human hair but significantly stronger than steel.
Manufacturing Process
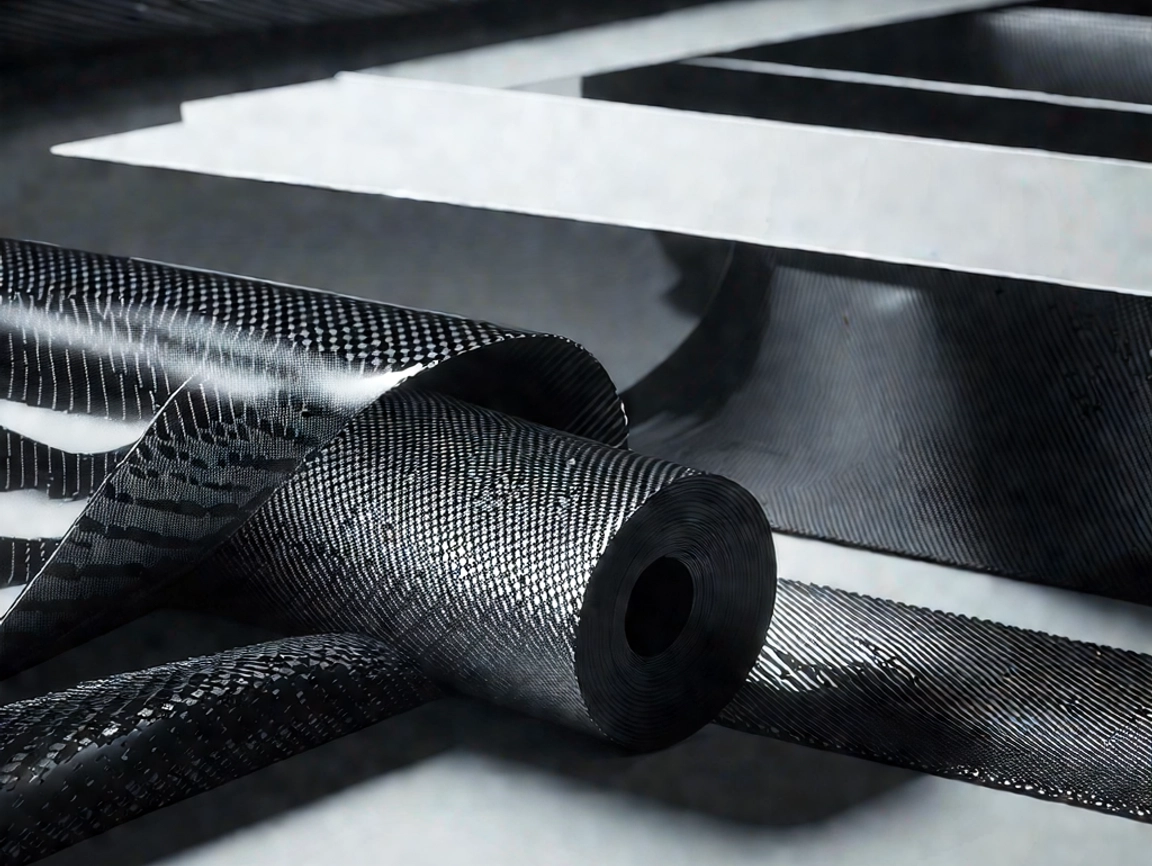
The production of carbon fiber is a complex process that transforms organic precursors, such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN) or pitch, into pure carbon strands through high-temperature treatments. The general manufacturing steps include:
- Stabilization (Pre-oxidation) – Heating PAN fibers to around 200-300°C in an oxygen-rich environment to alter their molecular structure.
- Carbonization – Further heating the fibers to 1,000-2,000°C in an inert atmosphere, eliminating non-carbon elements and forming tightly bonded carbon chains.
- Graphitization (Optional) – For some high-performance applications, fibers are heated beyond 2,500°C to enhance strength and conductivity.
- Surface Treatment and Coating – The fibers undergo chemical treatments to improve bonding with resins, followed by a protective coating for handling.
Properties of Carbon Fiber
Lightweight
One of the most significant advantages of carbon fiber is its weight efficiency. It is about five times lighter than steel and twice as light as aluminum, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial.
High Strength and Stiffness
Carbon fiber has an exceptional tensile strength, typically five times stronger than steel. It also boasts superior stiffness, making it a preferred material for structural applications requiring rigidity and durability.
Corrosion Resistance
Unlike metals, carbon fiber does not corrode when exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme weather conditions. This property makes it highly desirable for marine, aerospace, and chemical industry applications.
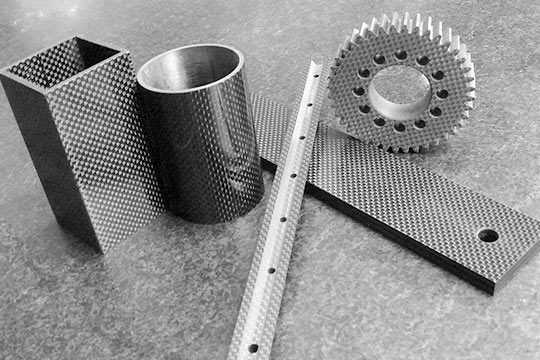
Applications of Carbon Fiber
Due to its outstanding properties, carbon fiber is widely used across various industries:
- Aerospace & Aviation – Aircraft components, satellites, and spacecraft structures.
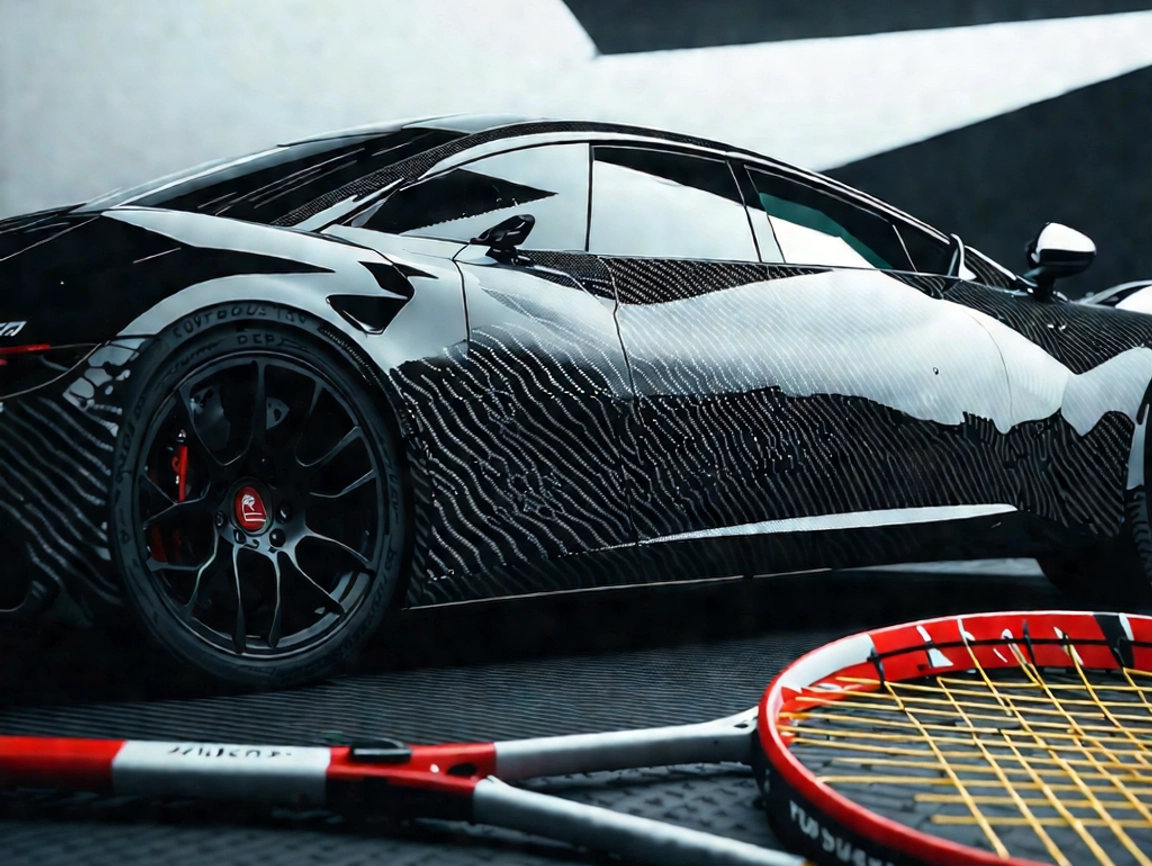
- Automotive – Lightweight and high-performance vehicle parts to improve fuel efficiency.
- Sports Equipment – Tennis rackets, bicycles, golf clubs, and racing helmets.
- Medical Devices – Prosthetics, surgical instruments, and advanced imaging equipment.
- Renewable Energy – Wind turbine blades and structural reinforcements in green technologies.
Conclusion
Carbon fiber is truly a game-changing material, combining lightweight properties with extreme strength and durability. As technology advances, its applications will continue to expand, revolutionizing industries and shaping the future of engineering and design. Whether in space exploration, automotive innovations, or high-performance sports, carbon fiber remains an essential pillar of modern technology.